Folding because of bad odds. If you are on a draw you should only call bets when you get the right pot odds and/or implied odds, as explained in more detail in the pot odds guide. As is mentioned in this guide it is very important to not overestimate your number of outs when deciding to draw or not (i.e., don't draw to gutshot straights on a. You should already be familiar with most of the made hands after reading the article on the Rules of Texas Hold'em: Go to the article: The Rules of Texas Hold'em The hands like two pair, three-of-a-kind, straights, flushes and even better hands are also called monsters, because they are generally very strong hands. If there are already many players in the pot and it is unraised, you can play the suited hands from late position. Otherwise it is correct to fold them. I even fold the non-suited hands from late position in unraised pots over 95% of the time. They just aren't good enough to play. If you want to win money, you should fold the cards that are likely to get you into trouble and cost you money. Betting before the flop. If you have a strong hand and you want to enter the pot, you should almost always make a raise. Go back to the sublime Texas Hold'em guide. There are a lot of decisions to be made when you play Texas Hold'em at Bovada Poker. But once your stack gets down to a certain size, your decision is relatively easy: Push or fold. That's because you don't have enough chips left to apply leverage if you attempt a standard open-raise.
Welcome to our Texas Holdem guide.
The idea behind this guide is to walk you through the basic rules and strategies to Texas Holdem. While a lot of sites have articles written on the same topics, they're not as easy to understand as ours. They're not packaged neatly into a handy guide like ours, either, leaving you to figure out what you should read and in what order.
So if you want to pick up the game of Texas Holdem quickly, and blend into any table you sit down at, this is the guide for you.
Our Holdem guide will be divided into 4 parts. We'll start with rules and end with basic strategies. In the first part of our guide, I'm going to explain the rules of Texas Holdem, what (hands) beats what, betting formats and betting basics for beginners. Everything you need to know to play your first game of Texas Holdem.
Texas Holdem Guide » Part 2 » Part 3 » Part 4
Good luck and enjoy!
Texas Holdem Rules
Your first task is to learn the rules of Texas Holdem. The game appears to be complicated because there are 4 rounds, each with a new card and opportunity to bet.
But trust me, it's not as complicated as you may think. I'm going to walk through a complete hand now. I'm sure you'll pick it up quickly.
Note: All my examples will use 5/10 blinds.
Pre Flop
Pre flop is the first stage of a Texas Holdem hand. This is when the cards are dealt, players bet and decide whether or not they want to be involved in the hand.
The first thing that will happen is the blinds will be posted. The blinds are essentially antes that create dead money and encourage players to play, as opposed to sitting around waiting for good hand.
There are two blinds that need to be posted; the small blind and the big blind. The small blind is the first player to the left of the dealer button. This player will post $5. The player to his left (and two seats to the left of the dealer button) is the big blind. This player posts $10.
Poker Texas Holdem Hands
That's it. The blinds will change each hand, as the dealer button moves around the table.
After the blinds have been posted, the dealer will give each player 2 cards, one at a time, starting with the small blind and moving clockwise around the table. Each players' 'hole cards' are dealt faced down.
After the cards have been dealt the first betting round will begin. The betting action starts with the player to the immediate left of the big blind, also known as the player under-the-gun or UTG. This player has the option to call the big blind, raise or fold.
Once the UTG player has acted, the action will continue clockwise around the table until each player has acted. Each player will have the option to call, raise or fold. The blinds will be the last players to act in an un-raised pot. The small blind will have the option to pay the difference between the small and big blind or 'complete,' and the big blind can check his option. Both players can raise, too, if they choose.
The pre flop action will end once all the players but one have folded, or two or more players have completed the betting round and are ready to see the flop.
The Flop
The flop is the first community round.
The first thing that will happen is the dealer will place 3 community cards in the middle of the table (face up). All players can use these 3 cards to make the best 5-card poker hand.
After the flop has been dealt, another betting round will start. On the flop (and all subsequent rounds) the betting action will start with the first remaining player to the left of the dealer button and move around the table clockwise.
The betting options include check, bet, raise or fold. This depends on the action that took place before each player acts. If you're not familiar with these betting options, I cover them in more detail below.
The betting round ends the same as pre flop. Either all but one player folds, or two or more players have ended the betting round and are ready for the next community card.
The Turn
The turn is also known as 4th street. It's the 4th community card dealt that players can use to make their poker hand.
The betting round on the turn is the same as the flop.
The River
The river is the fifth and final community card that players can use to make their hand. It's also known as 5th street. The betting action on the river is the same as the turn.
Showdown
After the betting round on the river, and assuming two or more players are still in the hand, there will be a showdown. Players will show their cards so that a winner can be determined.
The showdown is simple. In an un-raised pot, the first player to the left of the dealer button will show their hand first. In a raised pot, the first player to show their hand is the player who raised last on the river. Then the action continues clockwise around the table. Each player can muck their hand (not show), or if their hand is better (and they want to win the pot, they can show their hand.
Then the pot is awarded to the best hand.
That's an entire hand of Texas Holdem. Once the pot has been awarded the cards will be collected and reshuffled. The dealer button will move one seat to the left, new blinds will be posted and a new hand of Texas Holdem will be dealt.
What Hands Beat What in Texas Holdem
One thing that trips new players up is determining what hands beat what. It's real simple for Texas Holdem. Here are the winning hands, from best to worst:
- Royal Flush – AKQJT suited.
- Straight Flush – 5 cards in a row, all of the same suit. For example, 34567 suited.
- 4 of a kind – 4 cards of the same value. For example, 4444x.
- Full House – A 3 of a kind and a pair. For example, 3-3-3-2-2.
- Flush – 5 cards of the same suit. For example, A-8-5-4-2 suited.
- Straight – 5 cards in a row. For example, 5-6-7-8-9.
- 3 of a kind – 3 cards of the same value. For example, 3-3-3-x-x.
- 2 Pair – Example: 2-2-3-3-x.
- 1 Pair – Example: A-A-8-4-2
- High Card – Example: A-K-J-3-2
In Texas Holdem you can make these hands (and win) using any combination of the community cards and your hole cards.
If there is a tie the pot will be split. It will be split however many times is necessary. For example, if 3 players have 78 and they all have straights, each of them will earn 1/3 the pot.
If two or more players have the same type of hand, the better or higher hand will win. For example, an ace high flush will beat a queen high flush.
Betting Formats and Actions
Texas Holdem is played in several variations and betting formats. They'll impact the game in a number of ways including time, variance, dead money, betting caps and more.
In this section I want to take a couple of minutes to explain the different betting formats you'll come across. That way you can choose which type of game you prefer, and at the very least understand how they all work. I'll also explain the different betting options you have during each betting round in Texas Holdem.
What Kind of Betting Formats Are There in Texas Holdem?
Limit Betting – Limit (or fixed limit) betting used to be the most popular format before no limit took over. With this betting format there are a couple of things to be aware of.
On the pre flop and flop rounds, only the small bet ($5) is used. On the turn and river the big bet ($10) is used. And there is (usually) a cap of 1 bet and 3 raises for any round. This does vary from one casino to the next, though. Last thing — players can only raise one increment (small or big bet) at a time. In other words, if someone bets $5, you can only raise $5, to a total of $10.
Pot Limit Betting – What distinguishes pot limit betting from other formats is that the amount of money in the pot determines how much someone can bet. In other words, if there is $10 in the pot, the next player to act can't bet more than $10. If they put $10 in the pot, making the total $20, the next player to act can only bet $20. Every time the size of the pot increases, the amount of money the next person can bet also increases.
No Limit Betting – No limit Texas Holdem is the most popular version played today. There is no limit to how much someone can bet. And at any time a player can push their entire stack in middle, going 'all in.'
Note – For the pot and no limit betting formats, raises must be the minimum of the current bet to call. For example, if the amount to call is $10, the minimum raise must be $20. If it's $26, the minimum you can raise is to $52.
Blinds – The blinds are forced bets that the first two players to the left of the dealer must post before the cards are dealt. The first player is the small blind and posts the smaller of the two bets, and the second is the big blind, and this player posts the bigger of the two bets. In a cash game the blinds never change. However, in a tournament and sit and go the blinds will change every so often, usually every 5-20 minutes.
Antes – Antes are a forced bet that each player must post before they are dealt cards. This is in addition to the blinds. They're usually 10-20% the size of the blinds.
Caps – In a capped game players can only lose so much per hand. The amount you can lose per hand depends on the game.
Short, Standard, Deep Stacks – This refers to the maximum number of big blinds someone can buy in for (in a cash game). In short stack games the maximum is 40 big blinds. In standard games you can buy in for 100 big blinds and 150+ in deep stack games.
Blind Levels – You only have to worry about blind levels if you're playing a Texas Holdem tournament or sit and go. The blinds will start low, around 10/20 or 25/50, and increase every 5-20 minutes. Each tournament will have a different structures and time frames.
Betting Actions
These are the betting options you have during a betting round in Texas Holdem.
Fold – You decide not to play your hand and toss it into the muck. If you fold you cannot win the pot.
Call – You call the last bet made. In an un-raised pot, you call the amount of the big blind. If someone raises, you must call the amount they bet.
Raise – A raise must be in increments of the last bet made. For example, in an un-raised pot at 5/10, the minimum you can raise is 10, to a total of 20. However, if someone raises to 35 (total), your minimum re-raise must be 35, to a total of 70.
Check – Checking is like saying, I pass. You give up your turn to bet (unless someone bets and the action comes back to you). It is possible for every player to check and the betting round to end with no additional money put into the pot.
Betting Basics for Beginners
From experience, I can tell you that most beginners don't know how to bet correctly. They bet for the sake of it or for the wrong reasons. And when they do bet, their sizing is off, which doesn't accomplish their goals and/or wastes chips.
My goal for the last section of our guide is to go into detail about how betting works in Texas Holdem, and to put you on the path to making correctly sized bets.
Mistakes Beginners Make When Betting
Lets start with the biggest mistakes beginner Holdem players make when they bet. The biggest mistakes I see are:
- Beginners bet too big. (You don't want to bet too small, either, but instead find a balance.) The problem with betting too big is that at some point the extra chips don't do anything. In other words, at 5/10, betting 200 chips is going to do the same thing as betting 50. So why bet 200?
- Your bets are transparent. A mistake players make is bet small with their premium hands (to keep other players in the pot), limp with weaker hands they don't mind folding, and then betting huge with premium, but vulnerable hands. Betting like this makes it obvious to everyone what you have.
- Betting for no reason. Sometimes players bet just for the sake of it.
Beginners make other betting mistakes, too, but a lot of that falls under specific strategies. That's too much (and too advanced) for me to cover here.
How to (Size Your) Bet Correctly
With the common mistakes out of the way, lets look at the right ways and times to bet.
Pre Flop Bet Sizing
One of the concepts I want to drill into you is that you should only bet enough to get the job done. No more, and no less.
So how much do you bet preflop?
The standard is 3x the big blind. With blinds of 5/10, the standard raise will be to $30. Depending on the game and stakes you're playing, however, your bet sizing can vary from 2-5x. For example, in tournaments a min-raise (2x) bet is very common for the later stages. And in micro stakes games, you can usually get away with betting 4-5x with your premium hands and the other players won't know the difference.
Note: One important thing to keep in mind is that you want to keep your bet sizes as consistent as possible, especially the higher the stakes you play.
In the scenario that a player limps in before you act, the rule of thumb (if you choose to raise) is to raise 3x the big blind plus 1 big blind for every limper. For example, if 3 players limp into the pot at 5/10, you'd bet $60. I use the same rule of thumb for my 3-bets (re-raises), too.
Post Flop Bet Sizing
When you make a bet post flop your bets should (almost always) be in relation to the size of the pot. And the amount you choose to bet will depend on a number of factors including:

- Your opponent
- Your hand
- The board texture
- Your goal
To come back to my main point, only bet as much as you have to (when bluffing) and as much as you can (when betting for value). And these should blend (balance) as much as possible, so that your opponents cannot tell the difference. That way you don't give away any information that can be used against you.
To give you an example:
On a drier flop (like A-T-3 rainbow) with 125 chips in the pot, a continuation bet of 75 chips is reasonable. If the flop is wet (has a lot of draws possible), then betting closer to 100 chips will work.
One thing you don't want to do is over bet the pot. For example, if the pot has 500 chips in it, your bet should be less than 500 chips. I wouldn't bet 550, 700 or shove all in (like many beginners do), regardless of the hand you have, or how vulnerable it may be. Betting close to the size of the pot is inducing enough mistakes from players on a draw as is, so only bet as much as you have to. There are exceptions, but these are advanced topics and not something I'd worry about right now.
Effective Stacks
One important concept to understand is effective stacks or effective stack sizes. You want to understand this concept because it will impact when and how much you bet.
To determine the effective stack size, just find the lowest stack size of the remaining players to your left. For example, if there are 5 players to your left and the shortest stack has 15 big blinds, that means effective stack sizes are 15 big blinds.
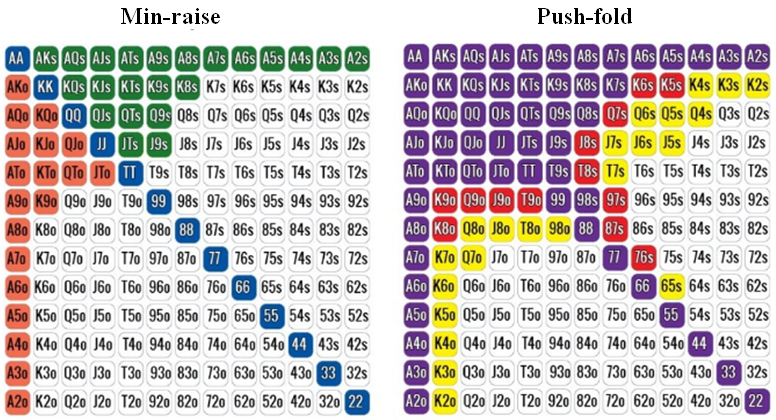
In this particular example, with effective stack sizes of 15 big blinds you might choose to fold your hand or push all in, as opposed to raising. However, if effective stack sizes are 50 big blinds, then you can resort to your default (betting) strategy. If effective stacks are 150 big blinds, then you'll play a wider range of hands and will bet (and re-raise) more.
That's the basic idea. It does get more complicated than this. But I wanted to give you the basics so that you can determine for yourself when it might make more sense to fold, raise or shove all in.
Have a Reason or Goal to Bet
If you're ever questioning when you should bet, just remember that there are only 3 reasons for betting:
- Value – You think/know you have the best hand and you want to earn as many chips as possible.
- Dead Money – Money that is already in the pot, either from antes, blinds, players who folded or a combination of these things.
- Bluff – You want the other player(s) to fold the better hand.
These are the only reasons for betting. Many players make the mistake of thinking that you should bet for information or to protect your hand. However, these reasons are byproducts of the reasons I outline above. If you're betting to protect your hand, you're usually betting for value. You're getting value from hands that are drawing. If you're betting for information, that's usually a byproduct of all 3 reasons above. You'll get your information based on what your opponent does.
The bottom line – if you're thinking about betting, but you can't decide if you should bet for value, dead money or to bluff, then you probably don't have a good enough reason to bet and should check, call or fold instead.
Conclusion — End of Part 1 of Our Texas Holdem Guide
That's it for the first part of our guide. You just learned enough to go play for your first game of Texas Holdem, not to mention disguise the fact that you're a beginner. And if you are confused about anything I discussed here, just re-read the guide again. You'll also find that any question you may have will be cleared up once you play a couple of hands.
In the next section of our guide I'm going to explain why you should pay attention at the table, whether you're in the hand or not, as well as how to classify your opponents and how different types of opponents will impact your strategy. Following that we're going to get into some math. I'm going to show you how to count poker outs, calculate card odds and pot odds so that you can correctly determine when you're (profitably) drawing to a better hand.
Poker is a lot like sex. Everyone thinks they are the best, but most don't have a clue what they are doing. — Dutch Boyd
It is very true, but hopefully by and reading our Texas Holdem Strategy section you will at least have a clue how to do well at one of them!
One of the great benefits of poker is that it is quite easy to learn the basics. The rules are quite simple and allow easy access for beginners. However, on the other hand, it is a tough game to master; there's always something to improve upon or learn.
The basic strategy below should provide you with the groundwork for developing a dominant poker game. We link to some more advanced material throughout for anyone that is further ahead of the trend.
Get the PDF version of the complete Poker 101 guide for offline use (30+ pages of poker goodness). Use one of the buttons below to unlock:
Thank you for your support. Get your Poker 101 Guide here.
Table Of Contents
- Preflop Texas Holdem Strategy
- Starting Hand Types
- Postflop Texas Holdem Strategy
- Texas Holdem Strategy: Betting and Raising
Preflop Texas Holdem Strategy
Your preflop poker strategy forms the foundation of your game. Your first decisions will be made preflop during a hand, so it is important to get these decisions right. Thankfully this is one of the easier areas of the game to understand.
So to help you understand let's take a quick example (click the picture to see the full replay):
We have JTs (J = Jack, T = Ten and the ‘s' after JT means both cards are of the same suit. An ‘o' after the JT would refer to off-suit)in the first position under the gun (UTG) on a six-handed table with $1/$0.5 BB and SB. We have to decide what to do: we can raise, call (otherwise known as a limp) or fold. There are a huge number of factors which we need to take into account, and unfortunately, I won't be able to cover them all. But I will try to cover the most fundamental factors in the coming paragraphs.
Firstly, it is very common to see new players play too many hands. They believe that they can outplay their opponents post-flop and turn a profit even with the weakest hands. This belief isn't the case and often is the main reasons a new player loses money when starting out.
Only Play A Small Percentage Of The Hands You are Dealt
Thus the first preflop poker strategy tip is to play only a small percentage of the hands you are dealt – the type of hands to play will be discussed further on in the text. Players who play a small selection of the hand they are dealt are referred to as tight. Conversely, players who play lots of hands are known as loose.
The vast majority of winning poker players are relatively tight, and for the most part, losing players are loose. Therefore, the first important poker strategy tip:
Preflop Poker Strategy Tip 1: Only play a small percentage of the hands you are dealt.
Luckily, JTs is in the top 12% of hands and therefore is a hand we would want to continue with, in this case. We can determine ‘how strong' a hand is using a program called Equilab. So our options are now to raise or to call because our hand is too strong to fold.
This result leads onto a second reason new players are unsuccessful – frequent limping
Limping is defined as calling the big blind instead of raising or folding. For example, you are first to act after you have been dealt two aces (AA) or like our example with JTs and instead of raising, you just call – this is called a limp.
Limping: Flawed Reasoning
Often, new players limp to see a cheap flop with speculative hands or to trap with strong hands such as AA or KK. Good winning players very rarely limp and there are many reasons why:
- You give the other players a chance to beat you with their weak holdings. For example, if you limp with AA and your opponent in the big blind checks behind he will have a chance to outdraw you to three of a kind or two-pair. Do not give people a free chance to improve and beat your strong hands.
- Raising with good hands builds the pot. A big hand deserves a big pot! Typically the only way you will win an opponent's whole stack (all of their chips) is by raising preflop; winning their entire stack is what you want when you have AA or KK, right?
- It allows you to better understand what your opponent may have. If we limp in and our opponent is in the big blind, he could have every possible hand; however, when we raise our opponent will fold some of the worse hands and the type of hands he can have become more defined. Experienced players use this to their advantage.
- Playing speculative hands (hands which could potentially, but infrequently win a big pot) such as 64s (s = suited, o = offsuit) and T2s just is not profitable in the majority of cases, whether you raise or limp, and no matter how good you are at poker.
Preflop poker strategy Tip 2: Never limp preflop
Example: JTs Under the gun
Since limping (i.e. just calling) is not an option our only option is to raise. That poses the question of how much? In this case, we will raise to 3x the BB, so $3 and one player calls our bet as shown. We will cover the reason we use 3x later in the article.
Three times the BB is a standard raise size which we will go into later in this article under the heading 'Texas Holdem betting strategy'. But first, a little more on aggression to drive home the point:
You should only raise or fold your hands when first entering the pot. However, calling with some hands after someone else has raised is fine. There are some situations where open limping is a good idea but they are so few and far between that never limping is a good starting preflop poker strategy – especially for a beginner.
This leads to another generalization of how people play poker:
Aggressive vs. Passive
In poker, an aggressive opponent is a player who bets and raises frequently. A passive opponent is a player who calls and checks often and very rarely bets or raises.
When Should I Fold In Texas Hold'em
Aggression is one of the keys to success in poker for one simple reason: When you bet or raise, you have two ways to win the pot – either your opponent folds or you get to showdown with the best hand.
Unfortunately, when a player is passive there is only one way to win the pot – by having the best hand. This difference is hugely important and is the reason all big winners are aggressive poker players; while most losing poker players are quite passive.
Preflop poker strategy Tip 3: Take the initiative and be aggressive. Bet and raise your strong hands frequently and don't rely on others to do the betting for you!
The four playing styles
In total there are four player styles:
- Tight-Aggressive (TAg) – This player type which makes up the majority of the winning player pool. They wait for strong hands and bet and raise them hard, punishing other players who play weaker styles.
- Loose-Aggressive (LAg) – successful loose aggressive players are few and far between. They play lots of hands and play them very aggressively. It is a tough style to play but also a tough style to combat!
- Tight-Passive – this player type does not play very many hands and when they do the play them by calling and checking frequently. These players lose their money slowly but surely.
- Loose-Passive – these player types just don't like to fold. Loose passive players play lots of hands – sometimes over 50% of the hands they are dealt. They are the complete opposite of tight-aggressive. This player type is the biggest loser and where the big winners make their money.
So what hands should you play? That is a difficult question to answer since it depends on many factors – what position you are in, how many opponents are on the table, how likely your opponents are to raise, the equity of your hand, how many BB you have and how many hands you have been raising recently.
Starting Hand Types
However, there are some basic starting hands that you should almost always be playing: Casino boat burns in florida keys.
Premium Hands
There are very few premium hands in poker but when we do get these hands we should be trying to build a pot as big as possible and as quickly as possible. These hands are:
AA, KK, QQ, JJ, and AK – the top pocket pairs and Ace-King. AK is considered to be a powerful hand because:
- It dominates all other strong non-paired hands (e.g. AQ and KQ),
- Against a pair, it's nearly a coin flip with approximately 45% pot equity (will win the pot 45% of the time if we are to go all-in preflop)
- It blocks AA and KK which are the only two hands which have a significant equity advantage.
These hand should always be raised and often re-raised to begin building the pot.
Strong Hands
Strong hands are hands you should also always be raised when first entering the pot. These hands should be called when someone has already raised before you. These hands include:
AQ, AJ, AT, KQ and 99-TT. Large suited and connected hands such as QJs, JTs, are also considered strong hands. Suited hands derive their strength from being able to make flushes. However, do not overestimate the value of suited hands. Don't play a hand just because it is suited. The value of a hand is derived from the combination of the ranks of the two hole cards. Example: AQ is much stronger than Q5, AQ is still much stronger than Q5 suited.
Preflop poker strategy tip 4: Do not overestimate the value of ‘suitedness.' Evaluate the strength of the hand from the rank of the two hole cards.
Medium Strength Hands
You need to be careful of this hand type. These hands can make you a big winner if correctly played, but when incorrectly played can cost you lots of chips. These hands include:
KJ, KT, QJ, JT and 22-88. Medium suited connectors such as 87s are also considered to be medium-strength hands.
You will play different hands from various starting positions. Details on this require a separate section – for more on the differences in the positions read position is king which will provide a 'beginners starting hand chart.
Summary Of Preflop Texas Holdem Strategy
In summary, preflop you should:
- You should play a small percentage of the hands you are dealt.
- Never limp.
- Take the initiative and be aggressive. Raise and Reraise your strong hands frequently and don't rely on others to do the raising for you!
- Do not overestimate the value of ‘suitedness.' Evaluate the strength of the hand from the rank of the two hole cards.
If all you take from this section is these four points you will still have significantly improved your chances of winning.
For a summary of preflop poker strategy see the video below:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UNgcJ4AmjGA
Postflop Texas Holdem Strategy
Once you understand right preflop Texas Holdem strategy, the postflop poker strategy becomes significantly easier. When you play weak hands from poor positions poker is quite difficult; nobody likes to play Q7 from out of position (Out of position means you act first, so your opponent will have more information than you)! However, if you play only a narrow range of hands from good starting positions, as is recommended, poker will become a much simpler prospect.
Postflop, there are many factors which we must take into account before we make a decision. The number of variables makes each decision quite complicated for a beginner. However, there are a few guidelines and concepts which can be understood which will help you in the decision-making process.
Postflop Poker Strategy – The Basics
One of the most important considerations is if we are in position (IP) or out of position (OOP). We will cover this in more detail in Position is king.
Secondly, we should be considering what our opponent may be holding. Does our opponent have only strong hands if he is a tight player? Does he play lots of hands meaning his ‘range' of hands will be quite weak? See more on how to hand read.
A whole book could be written on hand reading, so I won't go further into it. But it is important as a new player to begin thinking about what your opponent may have. Do not only consider the hand you are holding.
Postflop poker strategy Tip 1: Always consider what your opponent could be holding.
Next, we should consider the board texture. For example, is the board likely to have improved your hand or your competitors? Is the board likely to change very much on the turn or river? These considerations will be detailed further on in this guide.
Another consideration is how many players made it to the flop. If the flop is heads up (only you and your opponent) the strength of each hand is much better than if five or even six people made it to the flop. The more players that see the flop, turn, and river the less likely you are to win a showdown with a weak holding such as one pair. For more information on the differences between multiway and heads up pots, head over to pokernews.com.
Postflop poker strategy Tip 2: The more players there are in the hand, the less likely you are to win and the weaker your holding.
Finally, we need to consider how many chips are in the pot, how much we have left behind in our stack and how many chips our opponent has.
After these considerations, we can make a decision on how we are going to proceed in the hand.
So first let's have a look at board texture:
Postflop Poker Strategy: Notation
Before we discuss post-flop poker strategy and board composition in detail, we need to make sure the notation is clear to everyone.
In some cases, pictures will be used to show board textures, but often just text will be employed. When describing the board with text (i.e. letters and numbers), each card rank is represented by either its number or the first letter of its name. To take an example, the board:
This texture is described by 5♥ K♣ 5♦ and is often shortened to 5hKc5d. It is sometimes shortened further to 5K5r. Here the ‘r' means rainbow (the flop is all different suits). When the flop has a flush draw (i.e. not a rainbow board) the board could be represented by 5K5s. Here the ‘s' represents suited.
There are many types of boards, but in general, they can be broken down into two types: dry board textures and wet board textures.
Dry Board Texture
Dry board textures are ones which the players in the hand are less likely to have connected with the community cards. Also, dry also means a board which the strength of your holding is unlikely to change over the course of the hand.
Examples of dry board textures are:
Why are these boards considered dry? Well on the K55 board there are not many hands that will change the strength of your opponent's or your holdings. If for example, you held KQ, then the only way your opponent can now beat you is if he has:
Well on the K55 board there are not many hands that will change the strength of your opponent's or your holdings. If for example, you held KQ, then the only way your opponent can now beat you is if he has:
If for example, you held KQ, then the only way your opponent can now beat you is if he has:
- An Ax (e.g. Ace-Queen or Ace-Seven) hand and hits an ace on the turn or river.
- A pocket pair such as 77 which hits his set on the turn or river (unlikely).
- A hand such as QJ which hits a runner-runner straight (two cards in a row – for example, the turn is a Ten, and the river is an Ace resulting a straight Ten to Ace) or runner runner full house (two Queens or two Jacks).
The most important factor is that neither of these two board has many straight-draw or flush-draw possibilities. The lack of draws means that if you have a hand like A5 on the K55 board or 44 on the 742 board you are very unlikely to be beaten by your opponent if he is behind on the flop.
Additionally, dry flops are inherently difficult to hit and hence makes continuation betting as the pre-flop raiser (you raised first, and someone called your raise) especially useful on dry boards. Continuations bets will be detailed further on in this section.
Wet board texture
On the other hand, wet board textures are boards where the board is very likely to change over future streets.
Looking at the QT9s board, there are many cards which will modify the strength of many hands. If we have AQ or TT on this board we have a strong hand; but on many turn cards such as a K, J, 8 or any heart, the strength of these hands will significantly degrade. Also, there are many hand types that your opponent may have hit this board with:

- Your opponent
- Your hand
- The board texture
- Your goal
To come back to my main point, only bet as much as you have to (when bluffing) and as much as you can (when betting for value). And these should blend (balance) as much as possible, so that your opponents cannot tell the difference. That way you don't give away any information that can be used against you.
To give you an example:
On a drier flop (like A-T-3 rainbow) with 125 chips in the pot, a continuation bet of 75 chips is reasonable. If the flop is wet (has a lot of draws possible), then betting closer to 100 chips will work.
One thing you don't want to do is over bet the pot. For example, if the pot has 500 chips in it, your bet should be less than 500 chips. I wouldn't bet 550, 700 or shove all in (like many beginners do), regardless of the hand you have, or how vulnerable it may be. Betting close to the size of the pot is inducing enough mistakes from players on a draw as is, so only bet as much as you have to. There are exceptions, but these are advanced topics and not something I'd worry about right now.
Effective Stacks
One important concept to understand is effective stacks or effective stack sizes. You want to understand this concept because it will impact when and how much you bet.
To determine the effective stack size, just find the lowest stack size of the remaining players to your left. For example, if there are 5 players to your left and the shortest stack has 15 big blinds, that means effective stack sizes are 15 big blinds.
In this particular example, with effective stack sizes of 15 big blinds you might choose to fold your hand or push all in, as opposed to raising. However, if effective stack sizes are 50 big blinds, then you can resort to your default (betting) strategy. If effective stacks are 150 big blinds, then you'll play a wider range of hands and will bet (and re-raise) more.
That's the basic idea. It does get more complicated than this. But I wanted to give you the basics so that you can determine for yourself when it might make more sense to fold, raise or shove all in.
Have a Reason or Goal to Bet
If you're ever questioning when you should bet, just remember that there are only 3 reasons for betting:
- Value – You think/know you have the best hand and you want to earn as many chips as possible.
- Dead Money – Money that is already in the pot, either from antes, blinds, players who folded or a combination of these things.
- Bluff – You want the other player(s) to fold the better hand.
These are the only reasons for betting. Many players make the mistake of thinking that you should bet for information or to protect your hand. However, these reasons are byproducts of the reasons I outline above. If you're betting to protect your hand, you're usually betting for value. You're getting value from hands that are drawing. If you're betting for information, that's usually a byproduct of all 3 reasons above. You'll get your information based on what your opponent does.
The bottom line – if you're thinking about betting, but you can't decide if you should bet for value, dead money or to bluff, then you probably don't have a good enough reason to bet and should check, call or fold instead.
Conclusion — End of Part 1 of Our Texas Holdem Guide
That's it for the first part of our guide. You just learned enough to go play for your first game of Texas Holdem, not to mention disguise the fact that you're a beginner. And if you are confused about anything I discussed here, just re-read the guide again. You'll also find that any question you may have will be cleared up once you play a couple of hands.
In the next section of our guide I'm going to explain why you should pay attention at the table, whether you're in the hand or not, as well as how to classify your opponents and how different types of opponents will impact your strategy. Following that we're going to get into some math. I'm going to show you how to count poker outs, calculate card odds and pot odds so that you can correctly determine when you're (profitably) drawing to a better hand.
Poker is a lot like sex. Everyone thinks they are the best, but most don't have a clue what they are doing. — Dutch Boyd
It is very true, but hopefully by and reading our Texas Holdem Strategy section you will at least have a clue how to do well at one of them!
One of the great benefits of poker is that it is quite easy to learn the basics. The rules are quite simple and allow easy access for beginners. However, on the other hand, it is a tough game to master; there's always something to improve upon or learn.
The basic strategy below should provide you with the groundwork for developing a dominant poker game. We link to some more advanced material throughout for anyone that is further ahead of the trend.
Get the PDF version of the complete Poker 101 guide for offline use (30+ pages of poker goodness). Use one of the buttons below to unlock:
Thank you for your support. Get your Poker 101 Guide here.
Table Of Contents
- Preflop Texas Holdem Strategy
- Starting Hand Types
- Postflop Texas Holdem Strategy
- Texas Holdem Strategy: Betting and Raising
Preflop Texas Holdem Strategy
Your preflop poker strategy forms the foundation of your game. Your first decisions will be made preflop during a hand, so it is important to get these decisions right. Thankfully this is one of the easier areas of the game to understand.
So to help you understand let's take a quick example (click the picture to see the full replay):
We have JTs (J = Jack, T = Ten and the ‘s' after JT means both cards are of the same suit. An ‘o' after the JT would refer to off-suit)in the first position under the gun (UTG) on a six-handed table with $1/$0.5 BB and SB. We have to decide what to do: we can raise, call (otherwise known as a limp) or fold. There are a huge number of factors which we need to take into account, and unfortunately, I won't be able to cover them all. But I will try to cover the most fundamental factors in the coming paragraphs.
Firstly, it is very common to see new players play too many hands. They believe that they can outplay their opponents post-flop and turn a profit even with the weakest hands. This belief isn't the case and often is the main reasons a new player loses money when starting out.
Only Play A Small Percentage Of The Hands You are Dealt
Thus the first preflop poker strategy tip is to play only a small percentage of the hands you are dealt – the type of hands to play will be discussed further on in the text. Players who play a small selection of the hand they are dealt are referred to as tight. Conversely, players who play lots of hands are known as loose.
The vast majority of winning poker players are relatively tight, and for the most part, losing players are loose. Therefore, the first important poker strategy tip:
Preflop Poker Strategy Tip 1: Only play a small percentage of the hands you are dealt.
Luckily, JTs is in the top 12% of hands and therefore is a hand we would want to continue with, in this case. We can determine ‘how strong' a hand is using a program called Equilab. So our options are now to raise or to call because our hand is too strong to fold.
This result leads onto a second reason new players are unsuccessful – frequent limping
Limping is defined as calling the big blind instead of raising or folding. For example, you are first to act after you have been dealt two aces (AA) or like our example with JTs and instead of raising, you just call – this is called a limp.
Limping: Flawed Reasoning
Often, new players limp to see a cheap flop with speculative hands or to trap with strong hands such as AA or KK. Good winning players very rarely limp and there are many reasons why:
- You give the other players a chance to beat you with their weak holdings. For example, if you limp with AA and your opponent in the big blind checks behind he will have a chance to outdraw you to three of a kind or two-pair. Do not give people a free chance to improve and beat your strong hands.
- Raising with good hands builds the pot. A big hand deserves a big pot! Typically the only way you will win an opponent's whole stack (all of their chips) is by raising preflop; winning their entire stack is what you want when you have AA or KK, right?
- It allows you to better understand what your opponent may have. If we limp in and our opponent is in the big blind, he could have every possible hand; however, when we raise our opponent will fold some of the worse hands and the type of hands he can have become more defined. Experienced players use this to their advantage.
- Playing speculative hands (hands which could potentially, but infrequently win a big pot) such as 64s (s = suited, o = offsuit) and T2s just is not profitable in the majority of cases, whether you raise or limp, and no matter how good you are at poker.
Preflop poker strategy Tip 2: Never limp preflop
Example: JTs Under the gun
Since limping (i.e. just calling) is not an option our only option is to raise. That poses the question of how much? In this case, we will raise to 3x the BB, so $3 and one player calls our bet as shown. We will cover the reason we use 3x later in the article.
Three times the BB is a standard raise size which we will go into later in this article under the heading 'Texas Holdem betting strategy'. But first, a little more on aggression to drive home the point:
You should only raise or fold your hands when first entering the pot. However, calling with some hands after someone else has raised is fine. There are some situations where open limping is a good idea but they are so few and far between that never limping is a good starting preflop poker strategy – especially for a beginner.
This leads to another generalization of how people play poker:
Aggressive vs. Passive
In poker, an aggressive opponent is a player who bets and raises frequently. A passive opponent is a player who calls and checks often and very rarely bets or raises.
When Should I Fold In Texas Hold'em
Aggression is one of the keys to success in poker for one simple reason: When you bet or raise, you have two ways to win the pot – either your opponent folds or you get to showdown with the best hand.
Unfortunately, when a player is passive there is only one way to win the pot – by having the best hand. This difference is hugely important and is the reason all big winners are aggressive poker players; while most losing poker players are quite passive.
Preflop poker strategy Tip 3: Take the initiative and be aggressive. Bet and raise your strong hands frequently and don't rely on others to do the betting for you!
The four playing styles
In total there are four player styles:
- Tight-Aggressive (TAg) – This player type which makes up the majority of the winning player pool. They wait for strong hands and bet and raise them hard, punishing other players who play weaker styles.
- Loose-Aggressive (LAg) – successful loose aggressive players are few and far between. They play lots of hands and play them very aggressively. It is a tough style to play but also a tough style to combat!
- Tight-Passive – this player type does not play very many hands and when they do the play them by calling and checking frequently. These players lose their money slowly but surely.
- Loose-Passive – these player types just don't like to fold. Loose passive players play lots of hands – sometimes over 50% of the hands they are dealt. They are the complete opposite of tight-aggressive. This player type is the biggest loser and where the big winners make their money.
So what hands should you play? That is a difficult question to answer since it depends on many factors – what position you are in, how many opponents are on the table, how likely your opponents are to raise, the equity of your hand, how many BB you have and how many hands you have been raising recently.
Starting Hand Types
However, there are some basic starting hands that you should almost always be playing: Casino boat burns in florida keys.
Premium Hands
There are very few premium hands in poker but when we do get these hands we should be trying to build a pot as big as possible and as quickly as possible. These hands are:
AA, KK, QQ, JJ, and AK – the top pocket pairs and Ace-King. AK is considered to be a powerful hand because:
- It dominates all other strong non-paired hands (e.g. AQ and KQ),
- Against a pair, it's nearly a coin flip with approximately 45% pot equity (will win the pot 45% of the time if we are to go all-in preflop)
- It blocks AA and KK which are the only two hands which have a significant equity advantage.
These hand should always be raised and often re-raised to begin building the pot.
Strong Hands
Strong hands are hands you should also always be raised when first entering the pot. These hands should be called when someone has already raised before you. These hands include:
AQ, AJ, AT, KQ and 99-TT. Large suited and connected hands such as QJs, JTs, are also considered strong hands. Suited hands derive their strength from being able to make flushes. However, do not overestimate the value of suited hands. Don't play a hand just because it is suited. The value of a hand is derived from the combination of the ranks of the two hole cards. Example: AQ is much stronger than Q5, AQ is still much stronger than Q5 suited.
Preflop poker strategy tip 4: Do not overestimate the value of ‘suitedness.' Evaluate the strength of the hand from the rank of the two hole cards.
Medium Strength Hands
You need to be careful of this hand type. These hands can make you a big winner if correctly played, but when incorrectly played can cost you lots of chips. These hands include:
KJ, KT, QJ, JT and 22-88. Medium suited connectors such as 87s are also considered to be medium-strength hands.
You will play different hands from various starting positions. Details on this require a separate section – for more on the differences in the positions read position is king which will provide a 'beginners starting hand chart.
Summary Of Preflop Texas Holdem Strategy
In summary, preflop you should:
- You should play a small percentage of the hands you are dealt.
- Never limp.
- Take the initiative and be aggressive. Raise and Reraise your strong hands frequently and don't rely on others to do the raising for you!
- Do not overestimate the value of ‘suitedness.' Evaluate the strength of the hand from the rank of the two hole cards.
If all you take from this section is these four points you will still have significantly improved your chances of winning.
For a summary of preflop poker strategy see the video below:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UNgcJ4AmjGA
Postflop Texas Holdem Strategy
Once you understand right preflop Texas Holdem strategy, the postflop poker strategy becomes significantly easier. When you play weak hands from poor positions poker is quite difficult; nobody likes to play Q7 from out of position (Out of position means you act first, so your opponent will have more information than you)! However, if you play only a narrow range of hands from good starting positions, as is recommended, poker will become a much simpler prospect.
Postflop, there are many factors which we must take into account before we make a decision. The number of variables makes each decision quite complicated for a beginner. However, there are a few guidelines and concepts which can be understood which will help you in the decision-making process.
Postflop Poker Strategy – The Basics
One of the most important considerations is if we are in position (IP) or out of position (OOP). We will cover this in more detail in Position is king.
Secondly, we should be considering what our opponent may be holding. Does our opponent have only strong hands if he is a tight player? Does he play lots of hands meaning his ‘range' of hands will be quite weak? See more on how to hand read.
A whole book could be written on hand reading, so I won't go further into it. But it is important as a new player to begin thinking about what your opponent may have. Do not only consider the hand you are holding.
Postflop poker strategy Tip 1: Always consider what your opponent could be holding.
Next, we should consider the board texture. For example, is the board likely to have improved your hand or your competitors? Is the board likely to change very much on the turn or river? These considerations will be detailed further on in this guide.
Another consideration is how many players made it to the flop. If the flop is heads up (only you and your opponent) the strength of each hand is much better than if five or even six people made it to the flop. The more players that see the flop, turn, and river the less likely you are to win a showdown with a weak holding such as one pair. For more information on the differences between multiway and heads up pots, head over to pokernews.com.
Postflop poker strategy Tip 2: The more players there are in the hand, the less likely you are to win and the weaker your holding.
Finally, we need to consider how many chips are in the pot, how much we have left behind in our stack and how many chips our opponent has.
After these considerations, we can make a decision on how we are going to proceed in the hand.
So first let's have a look at board texture:
Postflop Poker Strategy: Notation
Before we discuss post-flop poker strategy and board composition in detail, we need to make sure the notation is clear to everyone.
In some cases, pictures will be used to show board textures, but often just text will be employed. When describing the board with text (i.e. letters and numbers), each card rank is represented by either its number or the first letter of its name. To take an example, the board:
This texture is described by 5♥ K♣ 5♦ and is often shortened to 5hKc5d. It is sometimes shortened further to 5K5r. Here the ‘r' means rainbow (the flop is all different suits). When the flop has a flush draw (i.e. not a rainbow board) the board could be represented by 5K5s. Here the ‘s' represents suited.
There are many types of boards, but in general, they can be broken down into two types: dry board textures and wet board textures.
Dry Board Texture
Dry board textures are ones which the players in the hand are less likely to have connected with the community cards. Also, dry also means a board which the strength of your holding is unlikely to change over the course of the hand.
Examples of dry board textures are:
Why are these boards considered dry? Well on the K55 board there are not many hands that will change the strength of your opponent's or your holdings. If for example, you held KQ, then the only way your opponent can now beat you is if he has:
Well on the K55 board there are not many hands that will change the strength of your opponent's or your holdings. If for example, you held KQ, then the only way your opponent can now beat you is if he has:
If for example, you held KQ, then the only way your opponent can now beat you is if he has:
- An Ax (e.g. Ace-Queen or Ace-Seven) hand and hits an ace on the turn or river.
- A pocket pair such as 77 which hits his set on the turn or river (unlikely).
- A hand such as QJ which hits a runner-runner straight (two cards in a row – for example, the turn is a Ten, and the river is an Ace resulting a straight Ten to Ace) or runner runner full house (two Queens or two Jacks).
The most important factor is that neither of these two board has many straight-draw or flush-draw possibilities. The lack of draws means that if you have a hand like A5 on the K55 board or 44 on the 742 board you are very unlikely to be beaten by your opponent if he is behind on the flop.
Additionally, dry flops are inherently difficult to hit and hence makes continuation betting as the pre-flop raiser (you raised first, and someone called your raise) especially useful on dry boards. Continuations bets will be detailed further on in this section.
Wet board texture
On the other hand, wet board textures are boards where the board is very likely to change over future streets.
Looking at the QT9s board, there are many cards which will modify the strength of many hands. If we have AQ or TT on this board we have a strong hand; but on many turn cards such as a K, J, 8 or any heart, the strength of these hands will significantly degrade. Also, there are many hand types that your opponent may have hit this board with:
- Any 8 or K is an inside straight draw (4 cards will complete the straight).
- Any J is an open-ended straight draw (8 cards will make a straight)
- The majority of opponents plays Queens, Tens, and Nines.
Therefore, your opponent is likely to continue with a large proportion of his hands on this board.
We can directly translate all these points to the 432s board; except for the last as this board has cards of lower ranks. On the 432s board, however, every Ace has an inside straight draw. Aces will be played quite frequently by most opponents.
Every other board type will be somewhere in between the dry K55r and the wet QT9s. Understanding how wet or dry a board is and adjusting your strategy correctly is the key skill at play in this scenario. For more information on board textures, see this excellent article.
Continuation betting
A continuation bet, as its name suggests, is when you follow up on your previous aggressive action with another bet. For example, you raise pre-flop and then continue to bet on the flop. Continuation bets are extremely useful postflop poker strategy for two reasons:
- It is tough to connect with most board types; therefore player who bets first will often win the pot
- The player who last raised pre-flop will typically have the strongest hands; thus will get the benefit of the doubt when he bets again.
The rate at which you continuation bet should be, on a very basic level, determined by the wetness of the board.
The dryer the board, the less likely your opponent hit and therefore the more often we will want to bet so that we can take down the pot.
But we should also be more prone to bet when we have a chance to win the pot when called. In other words, we have pot equity in the form of a draw or overcards.
Postflop poker strategy Tip 3: The dryer a board texture, the more likely we are to win the pot by continuation betting (cbet).
Example 1: A Good Spot To CBet
So let's take a few examples of good examples of continuation bets. Continuation from our previous example of JTs from UTG (click the picture to see the full replay):
We opened to 3bb from UTG and got one call from the Button. On the flop of 9h7s3s, we have an inside straight draw and two overcards. This board is ranked medium for wetness and how the opponent connects; our opponent can have a few straight and flush draws as well as top pairs.
JTs is a good hand in this situation as we can make robust pairs on the turn and river and also can make the nut straight. Thus this is a good spot for a cbet as a bluff. We expect him to fold hands which are better than ours. However, if he does continue, we have a good chance of making a stronger hand with a J, T or 8.
We should keep bluffing to a minimum when playing small stakes and especially at play money poker. But in this case, it is almost a perfect situation for a bluff.
Example 2: Another good spot to CBet
Another situation for a good cbet is below:
We raised with 22 from the Button and got two callers from the SB and BB. Both check to us on the flop. This situation is a clear spot to value bet (value betting and bluffing are discussed in the next section). The flop is relatively wet, and two players can draw out us with straights and flush draws. Therefore, we want to charge them to see them next card.
Also, we have a robust hand (the second or third strongest depending on whether our opponents will re-raise KK preflop). We can get lots of value and win a big pot by betting; thus this is an excellent spot for a value bet.
Cbetting for value is a fundamental aspect of our postflop poker strategy and is one of the primary sources of profit at small stakes. Ensure you understand and utilize continuation betting fully by reading our in-depth article.
Example 3: A bad spot to Cbet
Below is a dangerous situation to continuation bet:
We raise a limper with 98s and get a call from the BB and the player who limped. The flop is terrible for us as we have a small amount of equity and this board is likely to have hit one of our opponents. Thus it is not a good spot to continuation bet (cbet), and we should check behind and fold to any future bets.
Postflop poker strategy Tip 5: Do not cbet on board textures where your opponent is likely to call, and you have little chance of improving on later streets
Continuation bets can also apply to the turn and the river. For example, we refer to betting the flop, turn and river as a continuation bet.
Continuation bets are how a significant proportion of your winnings will be generated at small stakes and free money poker. People often give up when they do not hit anything so take advantage of this fact.
Stack sizes
The number of chips you have bought in for or currently have on the poker table is known as ‘stack depth.'
If you are playing ‘short stack' poker, it means you are not playing with very many chips on the table – for example, 40bb. We do not recommend shallow stack play. Shallow stack poker means we have fewer chips on the table and hence we can win fewer chips from the weak poker players at the table.
Conversely, deep-stacked play means you have a lot of chips at the table – e.g. 200bb deep.
The shallower your stack depth, the more likely you should be to go all in. In poker terms going all-in is called ‘stacking off.'
Stack depth has a profound effect on your preflop and post-flop poker strategy so ensure you are aware of your stack depth at all times.
For example, it would be appropriate to allow yourself to get all in with post-flop with top pair good kicker such as KQ on K72 if you had a stack depth of 40bb; however, not if you had a stack depth of 100bb or greater.
Postflop poker strategy tip 5: The greater your stack depth, the stronger a holding you need to stack off. Always be aware of your stack depth before entering a pot.
Before playing a hand pre-flop, you should be checking the stack depth of you and your opponents. Checking stack depth ensures you understand how many chips are at play.
One mistake often made by new players is not considering effective stack size: if you have 100bb and your opponent has 40bb then the effective stack size is 40bb; this is because your opponent can win no more than 40bb from you. Hence your effective stack size can vary from hand to hand, and you must adjust your post-flop poker strategy accordingly.
For a summary of post-flop strategy see this video below:
Texas Holdem Strategy: Betting and Raising
Betting is the fundamental aspect of poker which makes it an exciting game to play. The ability to wager money as a bluff inducing your opponent to fold is one of the biggest selling points of the game; it is the first thing people think of when discussing poker!
But it's not all about bluffing as Hollywood has led you to believe. A lot of a winning Texas Holdem strategy just involves getting your bets in when you have a better hand than your opponent.
Poker betting strategy: reasons to bet
There are three reasons why one would want to bet:
- For value – to get worse hands to call meaning we will win a bigger pot. For example, you value bet AK on an Ace high board (such as A72) to get AQ, AJ, etc. and worse pairs to call.
- As a bluff – to get better hands to fold so we can win the pot with a poor holding. For example, you may be QJ on the A72 board to get hands such as non-paired Kings (KQ, KJ) to fold.
- As a semi-bluff – A semi-bluff is much like a natural bluff only that when we are called we will still have a good likelihood of winning the pot. With a semi-bluff, we have a lot of pot equity. An example of a semi-bluff would be betting or raising with a flush draw: a weak non-made hand which has the potential to make a robust hand. See more information on semi-bluffing.
Before betting, consideration should be made as to why a bet is being made. Can worse hands call our bet and provide us with value? Can we get better hands to fold? If neither is the case, you typically shouldn't be betting. This concept is integral to correctly implementing a solid poker betting strategy.
Poker Betting Strategy Tip 1: Always consider when betting, will your bet either get your opponent to fold a better hand (bluffing) or call with a worse hand (value betting).
This concept can difficult to grasp as a new player. But generally, you should be just betting with your strong hands; and if you are playing small stakes or especially free poker, keep bluffing to a minimum. People at low stakes or even play money poker do not fold; thus bluffing at these stakes is a complete waste of money.
Poker betting strategy: Bet sizing
Bet sizing is one of the most complicated parts of NLHE and is one of the most challenging aspects to grasp for a new player. For simplicity sake there a few rules to stick to which won't lead you too far wrong:
- Preflop raise to 3 times (3x) the BB with all hands you are opening. Do not vary your bet sizing depending on your hand strength. Changing your bet sizing based on your hand strength is a sure-fire way to let your skilled opponents what you are holding.
- The same applies when re-raising another player preflop, make your raise three times the initial raise. For example, a player in a 100Nl game might open to $3. In that case, when you re-raise him with your strong holdings such as AA or KK, make it $9.
- Postflop bet between 1/2 and full pot size bets. That means that if on the flop, the pot is $10 you should be betting between $5 and $10. Any smaller than that and your opponent can easily call with a lot of hands. Allowing your opponent to call with lots of hands means you miss value with strong hands; also, your opponent isn't likely to fold when you are bluffing. This is a bad result either way!
For a more advanced guide on poker bet sizing see: Pokerlistings.com
A big mistake new players often make is using the same bet size as the pot grows on each street. For example: betting 5$ into a $10 pot on the flop and then betting $5 into a $20 pot on the turn. Your bet sizes should be relative to the pot! As the pot grows so should the size of your bet. Think fractions, not dollar amounts!
Poker Betting Strategy 2: As a general rule always raise at least three times the previous bet or raise. When betting post-flop bet between 1/2 to a full pot-sized bet.
These bet sizing rules aren't optimal; they are approximations. However, they should provide you with solid groundwork to get you off to a good start in your poker career.
Once you begin to understand the merits of betting and raising and develop a more comprehensive poker betting strategy you can start to see when it is appropriate to deviate from these rules.
See this video on value betting for more information.
Further Reading
That's it for Texas Holdem Strategy. If you are really keen on learning poker quickly, we would suggest you check out our home page for more information to accelerate your poker learning.
There is still a lot to learn so here are some further reading:
Common poker mistakes.
Or return to poker 101?
Last updated: 26 October 2020